While Ping is one of the best known tools for network monitoring and troubleshooting, the IOS version has a set of options that make it even more useful than the Ping you might know from your desktop. For instance, IOS allows you to set the size of the datagram and the DF (Do not Fragment) bit, so you can test MTU (Maximum transmission unit) of a network path.
Ping officially stands for “Packet INternet Groper,” but that is a backronym with the name probably coming from the pinging sound of active sonar.
Ping is part of the ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) suite, and uses Type 8 (Echo Request) and Type 0 (Echo Reply) ICMP messages. Below is a Wireshark analysis of an ping request packet. 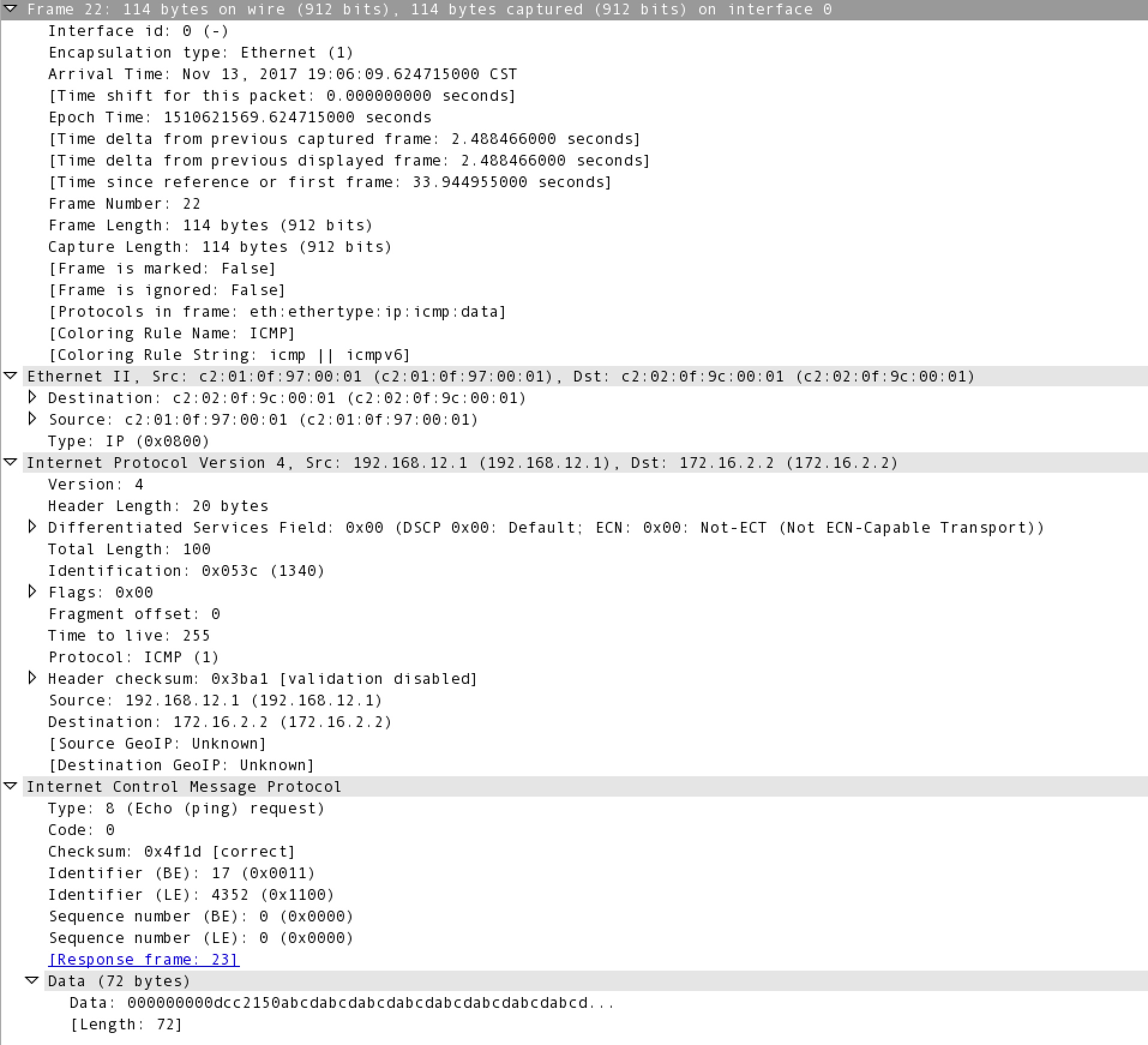
Note the Ethernet type of 0x0800 (IP), an IP protocol of 1 (ICMP), and and ICMP type of 8 (Echo Request). ICMP does not use TCP or UDP, it is it’s own protocol riding directly on IP.
To use Ping without the expended commands, you can just issue the ping command, followed by the ip address you want to ping.
R1#ping 192.168.13.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.13.3, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 44/102/312 ms
If you want to use the extended commands, you can add some of the options to the end of the ping command:
R1#ping 192.168.13.3 ? data specify data pattern df-bit enable do not fragment bit in IP header repeat specify repeat count size specify datagram size source specify source address or name timeout specify timeout interval validate validate reply data <cr>
Or issue the ping command, and hit enter, and IOS will prompt you for the other options. This allows for more options than are available as command line options, and walks you through the options you can set.
R1#ping Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: 192.168.1.1 Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5) R1#
The options for IP ping are as follows:
- Protocol – Although IP is the most common protocol, IOS Ping also supports appletalk, clns, decnet, ipv6, ipx, mpls, and srb.
- Repeat Count – How many ping requests should be sent? If you are looking for packet loss, it can be useful to send more pings. Five percent packet loss is one packet out of 20, so you may not see it reliably without sending hundreds of pings.
- Datagram size – the size of the packets to be sent. This can be quite useful for testing for network congestion, or a segment that has an MTU that is either preventing larger packets from passing through or causing delays due to fragmentation.
- Timeout in Seconds – How long to wait before considering a packet lost. 2 seconds should be fine for most uses, but it can be adjusted up or down to test for tighter requirements, or see if there is an inordinately long delay rather than a full outage.
- Extended Commands – Allows for the following extended commands.
- Source Address or Interface – by default, IOS sends internally sourced traffic, such as ping, traceroute, or outgoing telnet/SSH with a source IP of the outgoing interface. You can specify another interface, or an address assigned to an interface on the router. You may need to do this to test reverse routes, or test NAT or IPSec. You can either specify the interface or an ip address on the router for this.
- Type of Service – set a type of service to test QoS.
- Set DF bit in IP header – Set the Do not Fragment bit in the IP header to prevent transit routers from fragmenting the packet. The size where you start losing packets indicates the MTU somewhere along the path.
- Validate reply data – Validate the data in the reply packets. Could be useful for troubleshooting framing errors.
- Data pattern – Specify a HEX data pattern to use. This could also be used looking for framing errors.
- Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose. Specific options that can be added, definitions follow. Once you enter one, it will prompt you again, with the options entered in brackets. To proceed press enter again, or select another option.
- Verbose information (automatically enabled with the other options) displays more information, such as the time for individual pings, rather than just showing exclamation points (for successful pings) and periods (of lost pings)
- Record displays up to nine hops, but shows both the hops to and from the remote host, where traceroute only shows hops to the destination.
- Loose/Strict allows you to set IP addresses the packets should pass through. Strict requires the packet to take that route, while loose will attempt to pass those IPs, but can pass through others, as well.
- Sweep range of sizes – Set a minimum size, maximum size, and the size interval in bytes, and have IOS sweep the sizes to determine the MTU
Here is an example sweeping for the MTU. If you need more detail, you could run a sweep between the last successful size, 1500, and the first failed size, 1600, at a smaller interval to find an exact MTU.
R1#ping Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: 172.16.2.2 Repeat count [5]: 1 !only send one set of pings, or the sweep will be repeated. Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: yes Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: V Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[V]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: y Sweep min size [36]: 100 Sweep max size [18024]: 2000 Sweep interval [1]: 100 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 20, [100..2000]-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with the DF bit set Reply to request 0 (36 ms) (size 100) Reply to request 1 (116 ms) (size 200) Reply to request 2 (76 ms) (size 300) Reply to request 3 (48 ms) (size 400) Reply to request 4 (32 ms) (size 500) Reply to request 5 (8 ms) (size 600) Reply to request 6 (16 ms) (size 700) Reply to request 7 (28 ms) (size 800) Reply to request 8 (16 ms) (size 900) Reply to request 9 (32 ms) (size 1000) Reply to request 10 (12 ms) (size 1100) Reply to request 11 (32 ms) (size 1200) Reply to request 12 (16 ms) (size 1300) Reply to request 13 (28 ms) (size 1400) Reply to request 14 (4 ms) (size 1500) Request 15 timed out (size 1600) Request 16 timed out (size 1700) Request 17 timed out (size 1800) Request 18 timed out (size 1900) Request 19 timed out (size 2000) Success rate is 75 percent (15/20), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/33/116 ms
Summary:
Ping is a tool used to monitor and troubleshoot networks. It is based on ICMP, a set of protocols and tools built into the TCP/IP protocol stack. Any IP host should be able to respond to Pings, although some block it for security reasons.
IOS Ping allows an administrator to set advanced options, increasing its value as a troubleshooting tool.
The CCNA blueprint includes extended ping in the topics, so make sure you know this material, and that you take some time testing the the different options.
For more information on this, see:
